Ever faced a hepatic signal in a trial that looked like classic drug-induced liver injury (DILI), but turned out to be something entirely different?
Here’s a hypothetical scenario that might resonate, where hepatic physiology,
herbal pharmacology, and cultural practices intersected to produce a pseudosignal that mimicked hepatotoxicity.
A Complex Signal in an Early Phase Trial
During an early Phase trial of a novel drug, one site reported liver enzyme elevations in three participants from the high-dose cohort:
- ALT 2–3 × ULN
- Bilirubin: mildly elevated (1.2 × ULN) in one case
- No clinical symptoms, no jaundice, fatigue, or right upper quadrant pain.
It looked like hepatocellular injury, potentially qualifying as a Hy’s Law signal. But something didn’t add up.
The Hidden Variable: Herbal Co-Exposure
Upon deeper review of case narratives and follow-up interviews, the medical monitor discovered that the participants had been consuming traditional herbal decoctions:
- Andrographis paniculata
- Phyllanthus amarus
These were considered “health tonics” in the local culture and were not disclosed during standard medication history. Their omission was unintentional, these herbs were simply part of daily life.
Why Would These Matter?
Both herbs are pharmacologically active:
- Andrographolide, the key compound in Andrographis paniculata, is a known CYP3A4 inhibitor
- Phyllanthin and hypophyllanthin, from Phyllanthus amarus, inhibit CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and potentially conjugation enzymes like UGT
The mechanism likely involved:
- CYP enzyme inhibition
- Impaired clearance of the parent drug
- Accumulation of reactive intermediates
- Oxidative and mitochondrial stress in hepatocytes
- ALT/AST leakage
This wasn’t classic immune-mediated DILI, it was a pharmacokinetically driven pseudo-DILI, shaped by metabolic interference from herbal products.
Pharmacological Evidence (CYP Modulation) Andrographis paniculata
- Primary active compound: Andrographolide
Pharmacological Evidence (CYP Modulation) Andrographis paniculata
- Mechanism: Inhibits CYP3A4 activity (in vitro studies)
Reference:
Elza Sundhani, Endang Lukitaningsih, Arief Nurrochmad, Agung Endro Nugroho. Potential pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic herb-drug interactions of Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) and andrographolide:
A systematic review.
Phyllanthus amarus
- Active compounds: Phyllanthin, hypophyllanthin
- Mechanism: Inhibits CYP3A4 and CYP2C9
Reference:
Taesotikul T, Dumrongsakulchai W, Wattanachai N, Navinpipat V, Somanabandhu A, Tassaneeyakul W, Tassaneeyakul W. Inhibitory effects of Phyllanthus amarus and its major lignans on human microsomal cytochrome P450 activities: evidence for CYP3A4 mechanism-based inhibition. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2011;26(2):154-61. doi: 10.2133/dmpk.dmpk-10-rg-107. Epub 2010 Dec 17. PMID: 21178301.
Medical Monitoring Strategy
Once the pattern became clear, the safety team responded rapidly and decisively:
Pharmacokinetic (PK) Substudy
Goal: Determine if herbal co-use altered systemic exposure and metabolite profiles
- Used stored plasma samples
- Compared AUC, Cmax, and metabolite-to-parent ratios between herbalexposed vs. unexposed participants
- Analysis conducted using non-compartmental modeling
Key Results:
- Significant increase in AUC of parent compound in herbal users
- Strikingly higher metabolite-to-parent ratio
- Modestly extended half-life
Conclusion: Exposure was exaggerated due to impaired metabolism, likely contributing to hepatic stress, but not direct hepatotoxicity.
In Vitro Microsome Assay
Goal: Test direct inhibition of hepatic CYP enzymes by the herbal extracts
- Human liver microsomes used (pooled donor panels)
- Co-incubated with midazolam and diclofenac to probe CYP3A4 and 2C9 activity
- Enzyme kinetics analyzed via LC-MS/MS
Key Results:
- Andrographis extract inhibited CYP3A4 activity
- Phyllanthus extract inhibited both CYP3A4 and CYP2C9
- No CYP induction observed in PXR-based reporter assays
Outcome and Protocol Response
Following the findings:
- Dose escalation was paused temporarily
- CRF and ICF were updated to include herbal/traditional supplement disclosure
- A 14-day washout period was implemented for known hepatic modulators
- ALT/AST/bilirubin monitoring was intensified on Days 4, 7, 10, and 14
After herbal intake was discontinued, enzyme levels normalized within 10 days. No further cases were reported. The trial resumed with stronger hepatic safety controls in place.

Still Reflecting….
Even now, this scenario raises important questions:
- Are we doing enough to proactively uncover culturally “invisible” exposures in global trials?
- Are PK/PD insights being used early enough to differentiate real signals from pseudo-DILI?
- Are we integrating hepatic physiology, enzyme modulation, and cultural pharmacology into our signal detection framework?
This wasn’t just a pharmacovigilance issue. It was a clinical, cultural, and mechanistic puzzle; one that we solved by looking beyond lab values.

Let’s Keep the Conversation Going!
- Have you managed hepatic safety signals that turned out to be driven by cultural or dietary confounders?
- How do you screen for herb-drug interactions in early-phase settings?
- Let’s share ideas — because the more perspectives we hear, the better we can safeguard participants and protect the integrity of our science.

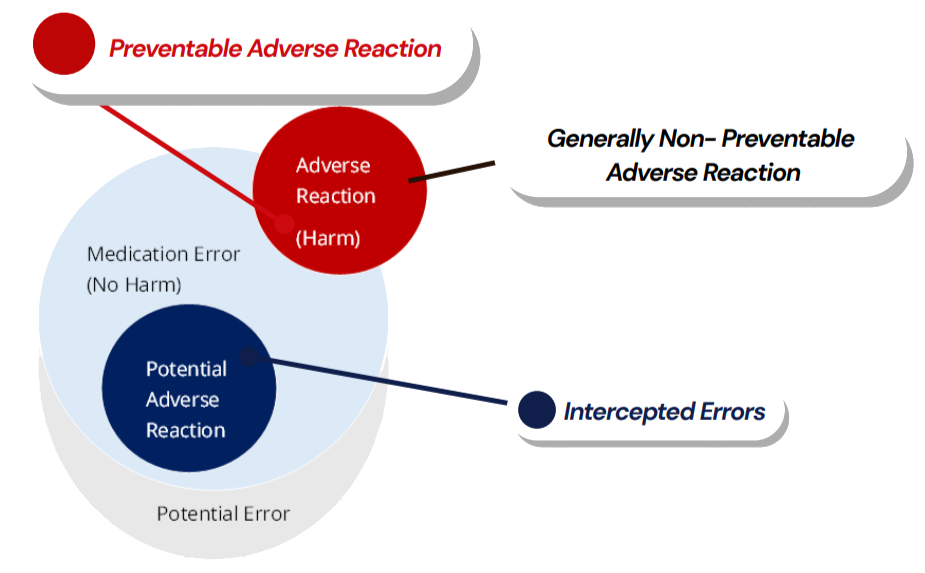
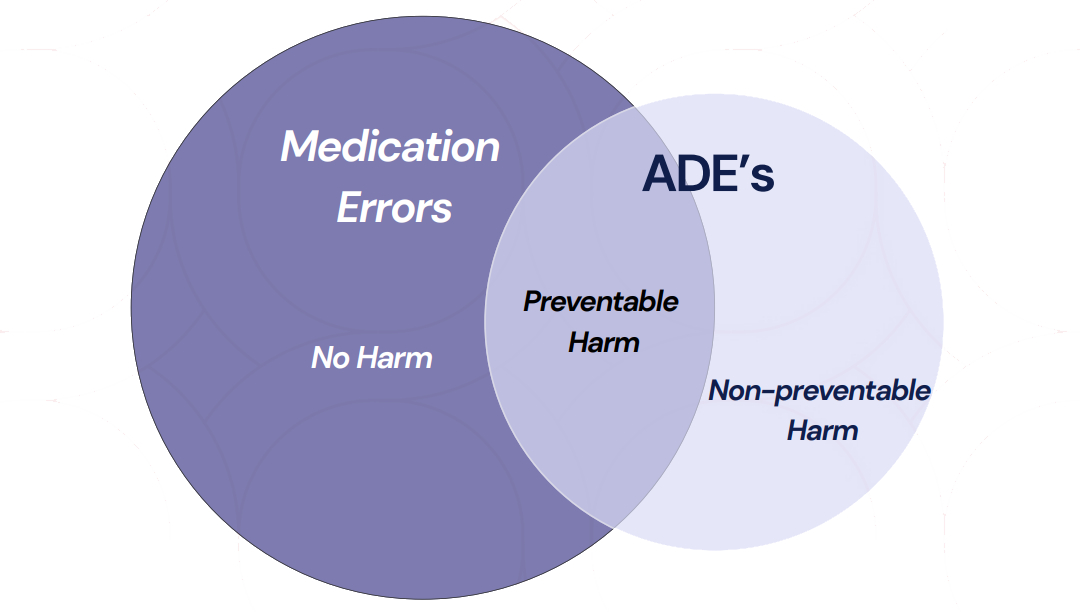
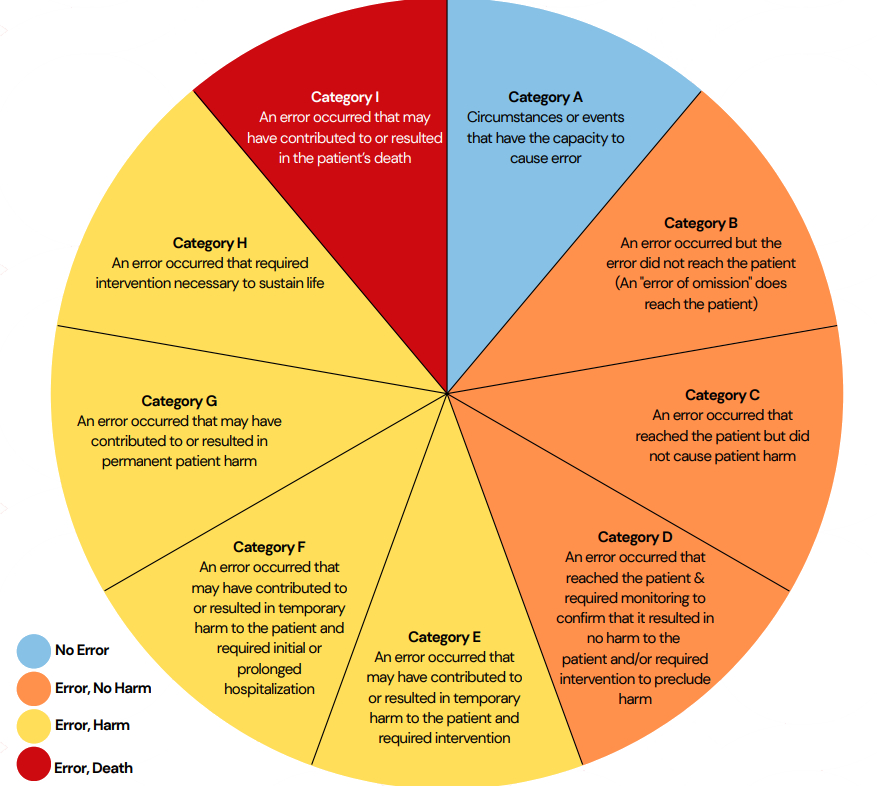
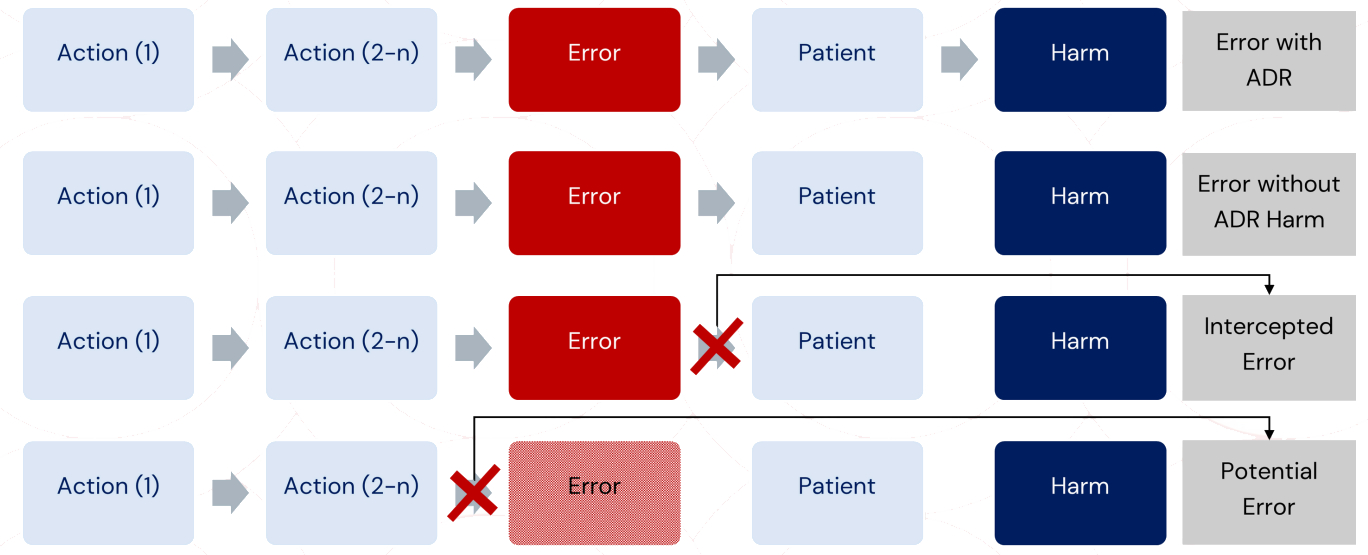 Ref: European Medicines Agency Good practice guide on recording, coding, reporting and assessment of medication errors. EMA/762563/2014
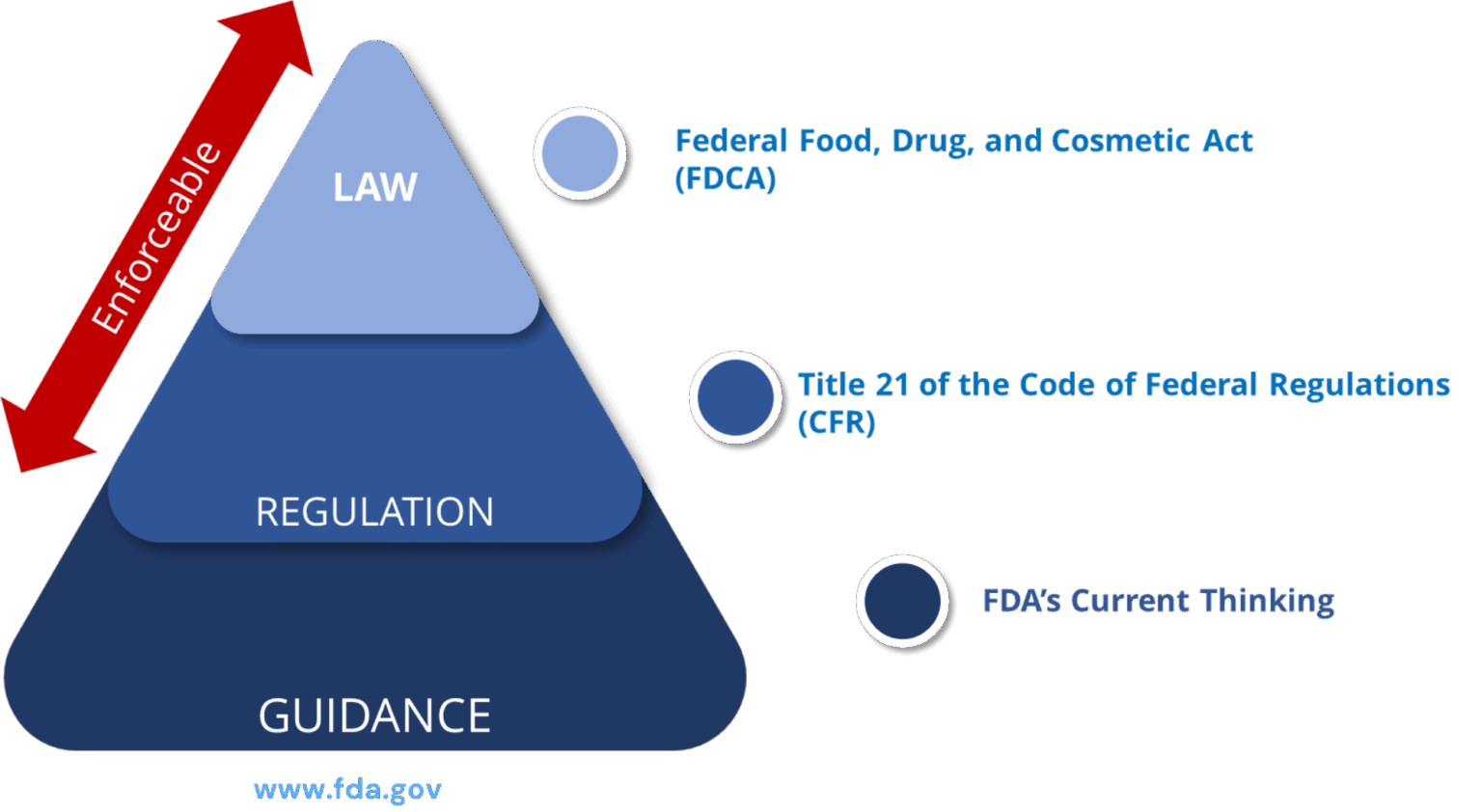
Ref: European Medicines Agency Good practice guide on recording, coding, reporting and assessment of medication errors. EMA/762563/2014